본 내용은 Coursera Build Basic Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) Lecture 기반으로 구성했습니다.
지난주, Coursera Andrew Ng 교수님의 Deep learning specialization을 마무리했습니다. 이번주부터는 굉장히 섬세한 fake 이미지를 생성할 수 있는 GAN 모델을 다루는 강의를 시청하고 리뷰할 예정입니다.
GAN 이란 Generative Adverarial Network의 약자로, 하나의 모델이 가짜 이미지를 생성하고 다른 모델이 진짜 이미지와 가짜 이미지를 구분? 하면서 Generator 모델이 더욱 완벽한 fake 이미지를 만들 수 있도록 training 합니다.
Generative Models
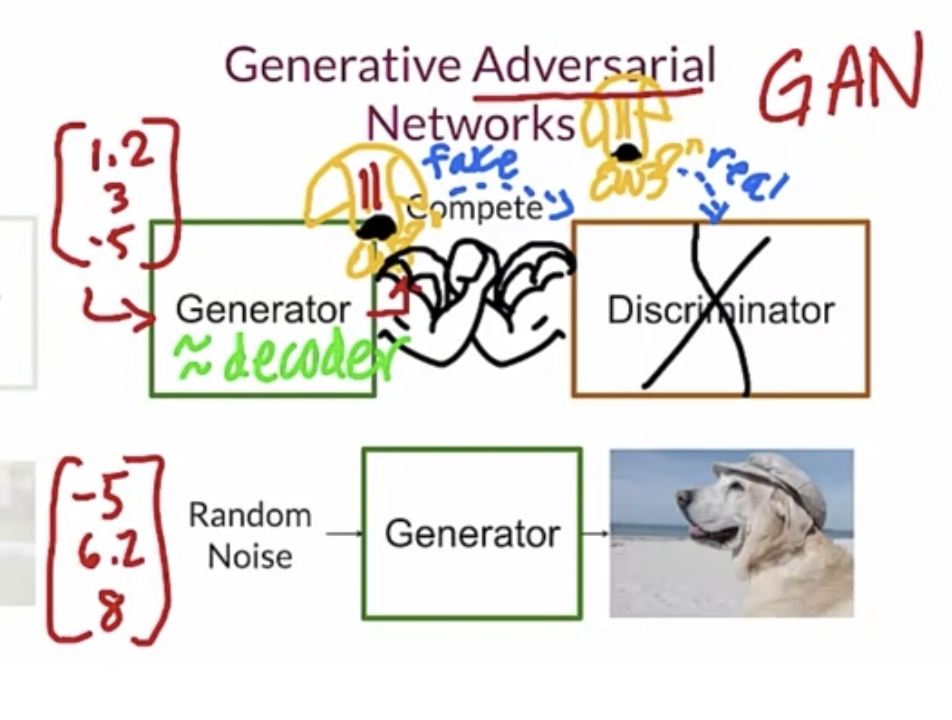
Generator
- Random noise를 input에 주고 fake image를 생성합니다.
Discriminator
- Real image를 input에 주고 학습시킵니다.
학습이 완료되면 Random Noise를 input으로 Generator에 주게 되면 정교한 fake 이미지를 생성하게 됩니다. 그리고 위 모델들이 경쟁하며 성능을 향상시키는 구조를 갖고 있습니다.
Summary
- Generative models learn to produce realistic examples
- Discriminative models distinguish between classes
Real Life GANs
Ian Goodfellow is known as the creator of the GAN.
not limited to human faces
image translation : horse to zebra, vice versa
draw something -> able to produce realistic image
Monariza -> moving
Companies Using GANs
- Adobe
- Google (text generation)
- IBM (data augmentation) : x enough data -> augmentation
- whatever you like
Summary
- GANs’ performance is rapidly improving
- Huge opportunity to work in this space!
- Major companies are using them
Intuition Behind GANs
Outline
-
the goal of the generator and the discriminator
-
the competition between them
Generator : learn to make fakes that look real
Discriminator : learns to distinguish real from fake
First, train a discriminator
Summary
- The generator’s goal is to fool the discriminator
- The discriminator’s goal is to distinguish between real and fake
- They learn from the competition with each other
- At the end, fakes look real
Discriminator
Outline
- Review of classifiers
- The role of classifiers in terms of probability
- Discriminator
Discriminator : Distinguish between different classes
Summary
- The discriminator is a classifier
- It learns the probability of class Y (real or fake) given features X
- The probabilities are the feedback for the generator
Generator
Outline
- What the generator does
- How it improves its performance
- Generator in terms of probability
Noise vector - different output
Noise -> Generator -> Features(X hat) -> **Discriminator ** -> Output (Y hat) -> Cost -> update Generator’s Parameters
Summary
- The Generator produces fake data
- It learns the probability of features X
- The Generator takes as input noise (random features)
BCE Cost Function
Outline
- Binary Cross Entropy(BCE) Loss equation by parts
- How it looks graphically
Summary
- The BCE cost function has two parts (one relevant for each class)
- Close to zero when label and the prediction are similar
- Approaches infinity when the label and the prediction are different
Putting It All Together
Outline
- How the whole architecture looks
- How to train GANs
Summary
- GANs train in an alternating fashion
- The two models should always be at a similar “skill” level
Intro to PyTorch
Outline
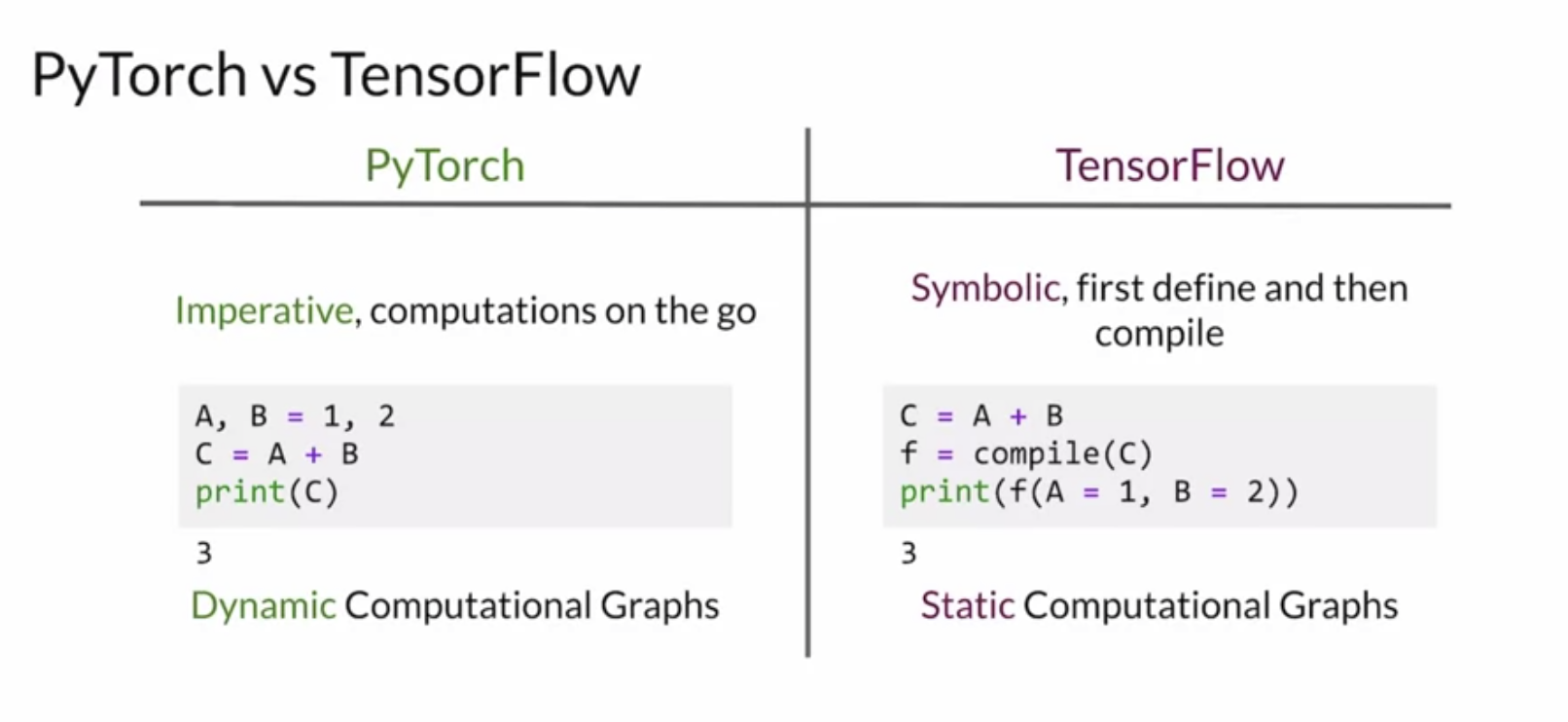
- Comparison with TensorFlow
- Dfining Models
- Training
Summary
- PyTorch makes computations on the run
- Dynamic computational graphs in PyTorch
- Just another framework, and similar to Tensorflow!

